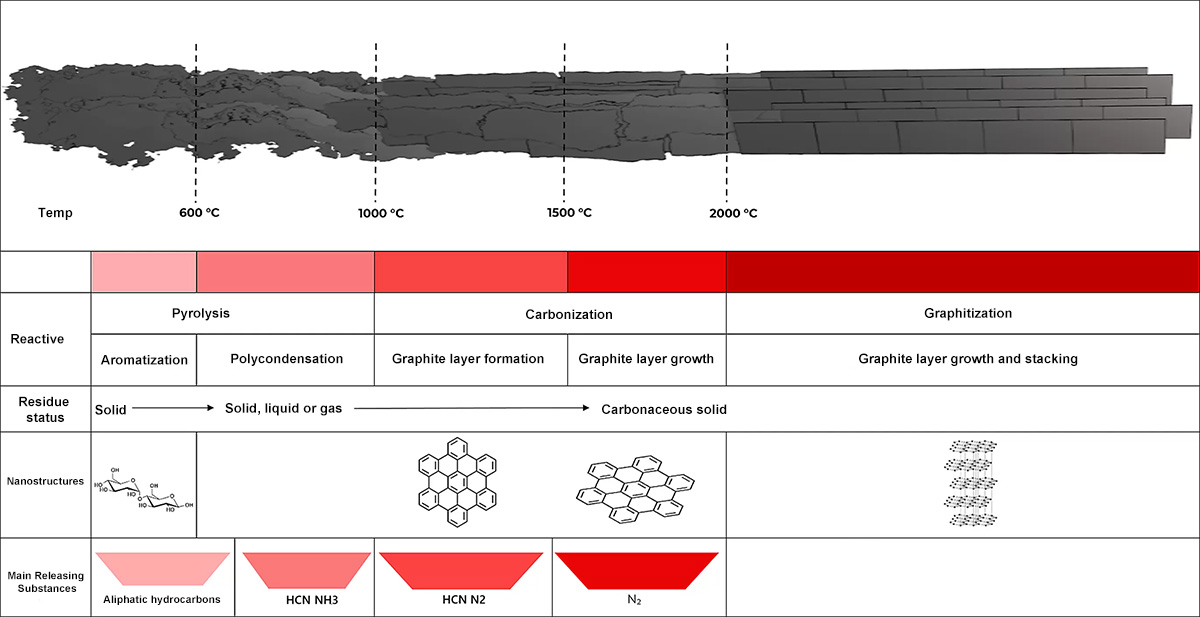
PAN-based raw wires need to be pre-oxidized, low-temperature carbonized, and high-temperature carbonized to form carbon fibers, and then graphitized to make graphite fibers. The temperature reaches from 200℃ to 2000-3000℃, which carries out different reactions and forms different structures, which in turn have different properties.
1. Pyrolysis stage: Pre-oxidation in the low-temperature part, low-temperature carbonization in the high-temperature part
Pre-oxidation arylation occurs, the length of nearly 100 minutes, the temperature of 200-300 ℃, the purpose is to thermoplastic PAN linear macromolecular chain into non-plastic heat-resistant trapezoidal structure, the main reaction for the macromolecular chain of cyclization and intermolecular crosslinking, accompanied by pyrolysis reaction and the release of many small molecules. The arylation index is generally 40-60%.
Low-temperature carbonization temperature is generally 300-800 ℃, mainly thermal cracking reaction, mostly using high-temperature electric furnace wire heating, the stage produces a large amount of exhaust gas and tar,.
Characteristics: The color of the pre-oxidized fiber will become darker, usually black, but still retains the morphology of the fiber, the internal structure has undergone a certain degree of chemical changes, the formation of a number of oxygen-containing functional groups and cross-linking structure, laying the foundation for the subsequent carbonization.
2. (High-temperature) carbonization stage, is the pre-oxidation of the precursor in an inert atmosphere at high temperature decomposition, removal of which in addition to carbon heteroatoms (such as oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, etc.), so that the gradual carbonization, the formation of amorphous carbon or microcrystalline carbon structure. This process is a key step in the formation of the carbon skeleton. The temperature is generally between 1000-1800 ℃, mainly thermal condensation reaction, most of the graphite heaters are used for heating.
Characteristics: The main component of the carbonized material is carbon, the structure is mostly amorphous carbon or chaotic graphite structure, its electrical conductivity, mechanical properties compared to the pre-oxidation product has a significant increase.
3. Graphitization is a further heat treatment of carbonization products at higher temperatures to promote the structure of amorphous carbon or microcrystalline carbon to a more orderly graphite crystal structure. Through the action of high temperature, carbon atoms are rearranged to form a hexagonal lattice layer structure with high degree of orientation, thus significantly improving the electrical and thermal conductivity and mechanical strength of the material.
Characteristics: The graphitized product has a highly crystalline graphite structure, which provides excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as high specific strength and specific modulus. For example, high-modulus carbon fibers are obtained through a high degree of graphitization.
Specific steps and equipment requirements for pre-oxidation, carbonization and graphitization:
Pre-oxidation: carried out in air at a controlled temperature of 200-300°C. Tension needs to be applied to reduce fiber shrinkage.
Carbonization: carried out in an inert atmosphere with a gradual increase in temperature to 1000-2000°C.
Graphitization: carried out at higher temperatures (2000-3000°C), usually in a vacuum or in an inert atmosphere.
Post time: May-22-2025